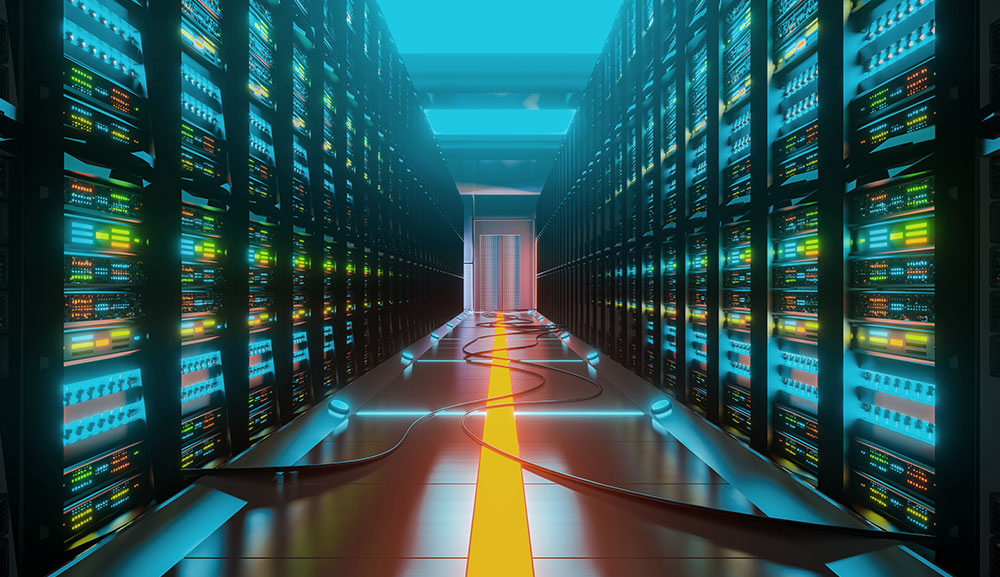
Network Topology Architecture is the way in which network devices such as computers, servers, routers, switches, and other devices are arranged, connected, and interacted with each other in a network. Network architecture refers not only to how devices are physically connected (Physical Topology) but also to how data moves through the network (Logical Topology).
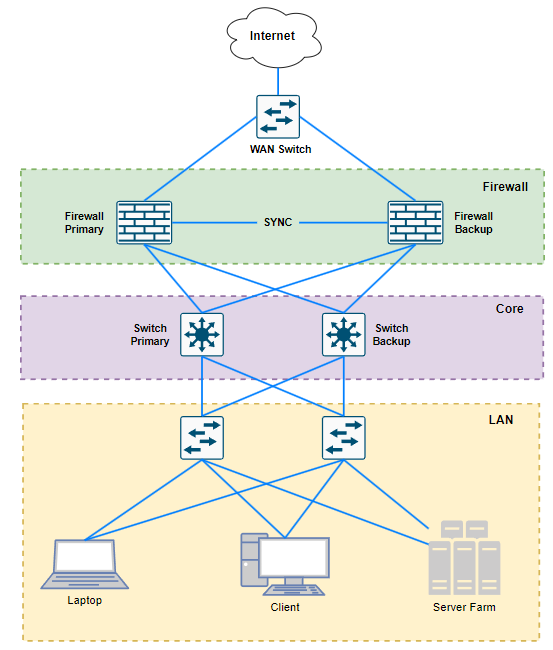
3 Tier Architecture
The 3 Tier Architecture, also known as the Three-Layered Hierarchical Model, is a traditional network architecture used in enterprise data centers. It divides the network function into three distinct layers, making it easier to manage and scale.
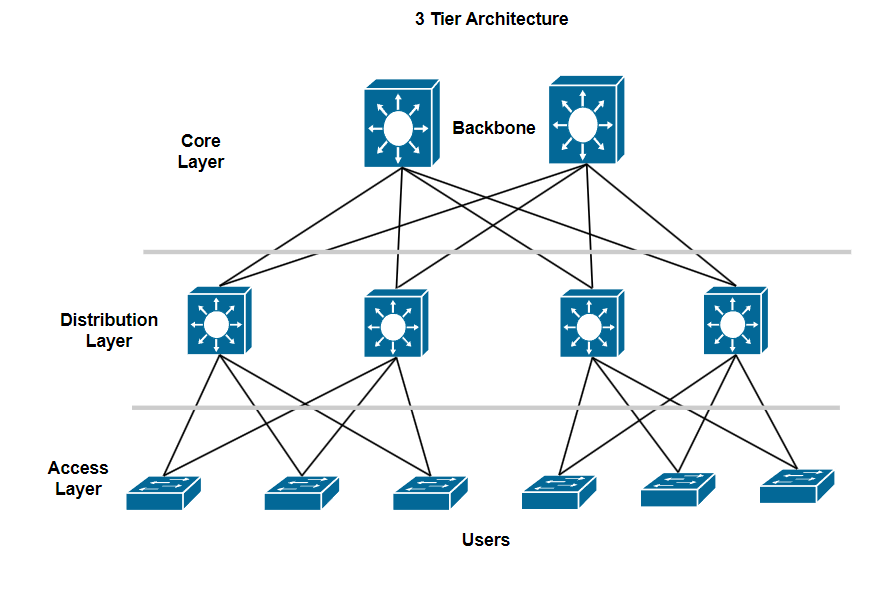
Core Layer
The Core Layer is the fastest and most powerful layer, providing a high-speed connection between the distribution layers. The Core Layer is typically located in the center of the network and is responsible for forwarding the largest traffic with the lowest latency.
The Core Layer ensures that data can move quickly and efficiently between different parts of the network, often connecting to critical systems such as servers and other data centers.
Distribution Layer
The Distribution Layer is the intermediate layer between the Access Layer and the Core Layer, which is responsible for aggregating traffic from Access switches and implementing routing policies, filtering traffic, and forwarding to the Core Layer.
The distribution layer can consist of switches or routers, and it provides services such as routing, access management, and inter-VLAN connectivity.
Access layer
The access layer typically consists of switches that connect directly to the user or device. These switches take care of managing the flow from the devices and bringing them to the distribution layer.
In the Access Layer including port security, loop protection STP, RSTP, PVST, MST are used in this layer. VLANs are used here to be able to divide the network.
2 Tier Architecture
The 2-Tier Architecture is a simple and efficient network architecture that is commonly used in small or medium-sized networks. Compared to the Three-Tier Architecture, this model eliminates an intermediate layer, which reduces the cost and complexity of network design and deployment.
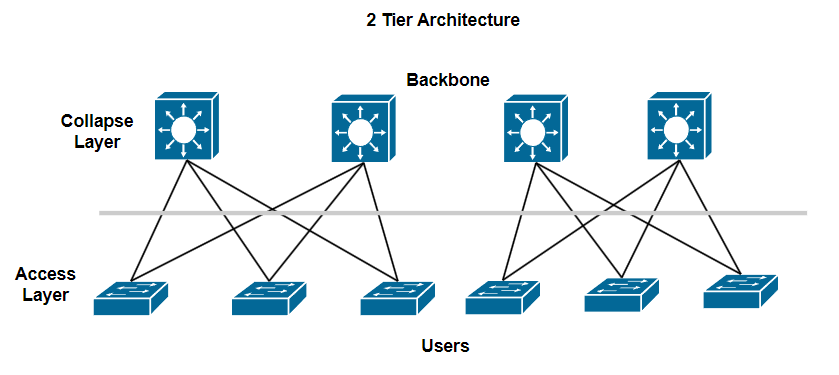
Collapse Layer
In the two-tier model, this layer combines the functionality of both the Distribution Layer and the Core Layer from the three-tier model. This layer is responsible for aggregating traffic from switches at the Access Layer and performing key network functions, such as routing and forwarding traffic.
This layer often uses high-performance switches or routers to ensure that traffic is processed quickly and efficiently. This layer also provides high-speed connections between different parts of the network and out of the WAN.
Access Layer
Like in the three-tier model, the access layer is responsible for connecting terminals such as computers, phones, and servers to the network.
The switches at this floor connect directly to user devices or end devices. This layer can include features such as Access Control Lists, VLAN partitioning, and traffic management.
Spine Leaf Architecture
The Spine-Leaf architecture is a modern network model, mainly used in large data centers. It is designed to provide high-performance, low-latency, and scalable connectivity, making it well-suited for cloud computing, large-scale web services, and environments that require rapid data exchange.
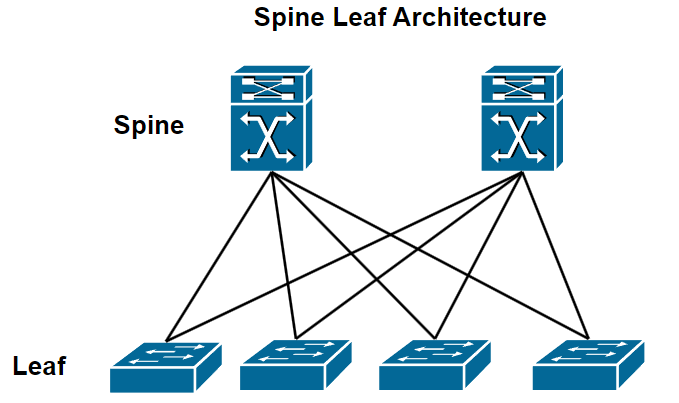
Spine
These switches form the second layer of the architecture and connect to all the switch leaf in the network.
Spine switches provide high-speed and high-capacity connections between leaf switches, ensuring that traffic can move efficiently across the network.
Leaf
These switches form the first layer of the architecture and connect directly to servers, storage devices, and other endpoints in the data center.
Each switch leaf is connected to all the spine switches in the network, ensuring that each server or device can communicate with any other device in the network with minimal latency.
Summary
Each network model has its own functions and is suitable for various needs. However, these network models are designed to make the design and deployment of a network system easier and more convenient. The article above highlights some common models found in companies and businesses today. This is fundamental knowledge for becoming a network engineer.


